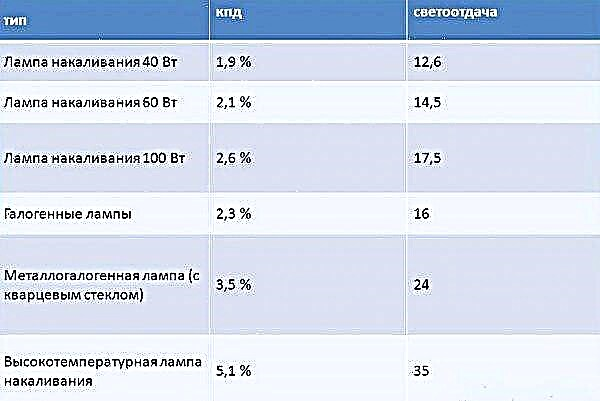
Incandescent lamps are sources of light, heat. Outwardly, it is a glass vessel with a tungsten spiral inside. The cavity itself in incandescent lamps is filled with inert gas. It prevents metal elements from oxidizing. When you turn on the electric current is conducted through a spiral, as a result of which there is heating and radiation of visible light.
Scope of use
Before the advent of energy-saving lamps, incandescent bulbs were used in industrial fields, household appliances, etc. Such an application was determined by the simplicity of installation and operation. But even now these lamps can be seen often:
- Indoor, outdoor lighting of rooms, streets, offices.
- Workplace lighting.
- Car bulbs.
- A small bulb of this type is also screwed into the lanterns.
- In public transport, trains, etc.
Specifications
The name of the indicator and its value are used to describe the characteristic.

These characteristics are given in the table:
| Name | Indicator |
| Power, W | domestic use - 25-150W, other - up to 1000 |
| Filament, degrees | up to 2000-2800 |
| Voltage | 220-330 |
| Luminous efficiency, Lm / 1W | 9-19 |
| Base size and marking | E 14, E 27, E 40 |
| Base Type | Threaded, pin |
| Opening hours | up to 1000 |
| Weight g | 15 |
The stated hours of work are carried out in the formation of optimal working conditions. Frequent on and off are not allowed.
Device and circuit
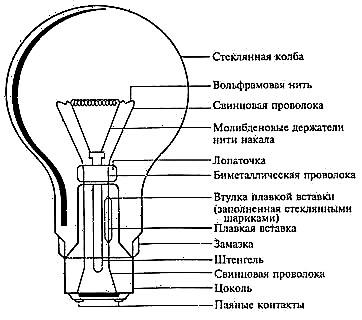
The device of an incandescent bulb in all its types is almost the same:
- The main workpiece is a tungsten spiral. It has resistance three times more than copper material. Melting of the finest elements is achieved from it. Electrodes support this spiral and transfer current.
- Glass flask. It is filled with inert gas. It is he who prevents the threads from burning and prevents the oxidation of metal elements.
- Basement. It is present in all forms except automotive. A thread is cut along the cap; its pitch may differ for each species.
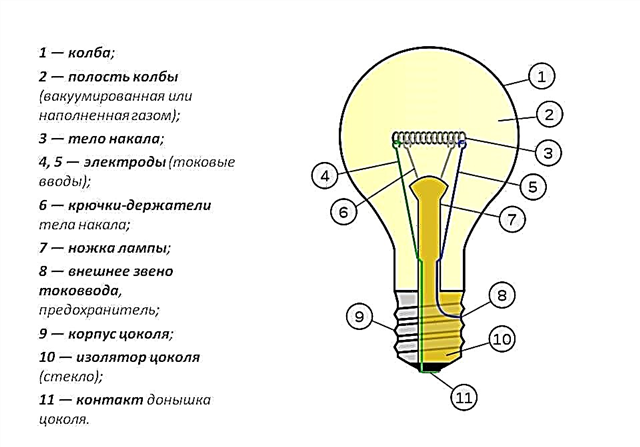
A detailed diagram of the components is shown in the figure:
Operating principle
The principle of operation of an incandescent lamp is to heat the substance through which current flows. The substance is the filament itself, its temperature rises at the moment of circuit closure. When this occurs, the result of electromagnetic thermal emission. It becomes visible to the eye when warming more than 570 degrees, while the red glow begins.
The filament is heated to 2800 degrees. In the process of heating, tungsten is converted into oxide (white surface coating), and for this, neutral gases are injected into the cavity. When installing the bulb (twisting it into a cartridge), the circuit closes and the process of heating the thread occurs, and light is supplied.
Cap
Commonly considered bulbs marked with a socle E14, E27, E40. Where the number means the diameter of the base itself. Without threaded elements are found in automotive industries.

There are countries where there is a different voltage in the network and, accordingly, bulbs with a different base diameter are used - E12, E17, E26, E39.
Marking
Before buying, you need to study the labeling. It is represented by a combination of letters and numbers. The letter marking and meaning are presented in the table:
| Letter marking | Value |
| B | bispiral |
| BO | Bispiral with an opal flask filled with argon |
| BC | Bispiral, flask filling with krypton |
| Db | Diffuse with frosting inside the flask |
| IN | Vacuum |
| G | Gas filled |
| ABOUT | Opal flask |
| M | Milk flask |
| W | Spherical |
| 3 | Mirror |
| MO | For local lighting |
The numbers indicate the limits of voltage, power.
Efficiency
These lamps have low efficiency (efficiency). It is expressed by the ratio of power to radiation, noticeable to humans. When heating the thread to 2700 K, the efficiency is up to 5 percent. The rest of the energy spent on infrared radiation, which is not visible to the human eye, is only felt by the heat. If you increase the efficiency to at least 20 percent, you need to increase the heating of the thread to 3400 K.

The light will shine twice as bright, but the lamp life will be reduced by 95 percent. And vice versa, reducing the voltage will increase the period of work by many times. All this is taken into account in the production of emergency lighting, which requires reliability.
Table of the ratio of lumens and watts in a light bulb
Luminous flux is measured in lumens (Lm). In LEDs, light fluxes fluctuate depending on the manufacturer, its product quality, voltage. The approximate value for one W is 80-150 Lm. The table shows the ratio of Lm and W for incandescent bulbs in relation to the LED lamp:
| LED lamp, W | Incandescent lamp, W | Luminous flux, Lm |
| 4-5 | 40 | 400 |
| 8-10 | 60 | 700 |
| 10-12 | 75 | 900 |
| 13-15 | 100 | 1200 |
Types of lamps and their functional purpose
The type of lamp is determined by the structural purpose, functional:
- Normal lighting is the most common form. Designed for general lighting and decorative. The release of this type is limited.
- Decorative - different sizes, with a figured glass flask. Appearance is very unusual, beautiful. Therefore, the application is special, decorative.
- Illumination - multi-colored exterior color. The tone is applied to the inside of the glass flask. Inorganic pigments are used for color. Outer color is very rare. By power limits up to 25 watts. The larger the operation, the more color and brightness changes.
- Signal - for illumination of light-signal devices. Now they are replaced by LED lamps.
- Mirrored incandescent lamps - a peculiar form. The inner glass surface is coated with a layer of aluminum. This gives a mirror to the product. The principle of operation - the light flux is distributed and collected in a specific area. Application: trading floors, shop windows, incubators (heating newborn chicks).
- Transport. Scope: headlights of the car, motorcycle, tractor, illumination. They differ in strength, vibration strength.
- Double strand. Applicable for car headlights. One thread for low beam, another for high beam. Also used in places where constant lighting is required, when one thread burns out, the second one works.
Advantages and disadvantages
Incandescent lamps have their own advantages and disadvantages.
- Ease of manufacture. Therefore, the price for them is appropriate.
- Ease of use. Installation of additional elements is not required when connected to the network. Often, 150 W lamps are used in lighting greenhouses. Their light is close to natural. In addition to lighting, they give heat.
- Does not affect human vision.
- It does not take time to warm up.
- Withstands temperature extremes.
- It is disposed of as household waste.
- The composition does not include harmful elements.
- Short service life.
- Dependence on interruption in the network, frequent on / off - this is the reason for the rupture of the spiral in incandescent lamps. To exclude difficulties with voltage, stabilizers are installed.
- Low level of efficiency. This is due to the consumption of most of the energy for heat.
- Fire hazard. As heat accumulates around the lamp.
- Fragility.
- There is a chance of a case breaking, which can lead to injury.
When buying an incandescent bulb, it is worth considering all the advantages and disadvantages in order to avoid unpleasant factors during operation.
We recommend watching the video:
Service life, cost
An incandescent lamp is influenced by many factors that contribute to reducing its life.
Recently, the quality of the light bulbs produced has fallen. Often the defect is immediately noticeable. Therefore, most buyers switched to buying goods from foreign manufacturers.
It is necessary to pay attention to the lamp holder, chandelier into which the lamp is screwed. In most devices, it is plastic, with increasing temperature it melts, crackes and becomes unusable. This affects the overheating of the bulb and failure.
Often, a reduction in operating time is due to the high voltage in the network. In this case, the incandescent filament overheats, it decreases in thickness, the bulb begins to darken. The spiral breaks. With a voltage deviation of only one percent, the lamp life is reduced by 14 percent.
The cost of a light bulb depends on the type, power, manufacturer. It ranges from 7 rubles to 100 rubles (for home consumption).
How to increase the service life
There are several ways to increase the life of the bulb:
- Dimmer setting. This simple device can extend the service life by several times. To do this, after connecting, the percentage of lighting is regulated. When lighting storerooms, porches, etc., it is enough to set the lamp performance to 75 percent.
- Since often failure is caused by power surges, it is enough to install a stabilizer.
What gas is in the lamp
The flasks of the product may not contain air or any gas. There should only be an inert gas (xenon, krypton, argon). This is due to the fact that the temperature of the spiral warms up to more than 2000 degrees.

At such temperatures, a tungsten filament will react with all gases except inert ones. Helium and neon are expensive, so they are not used.
Temperature
Light temperature depends on the type of gas injected. So, without a gas vacuum medium, it contributes to warming up to 2700 K. In this case, warm white light is emitted. When heated to 4200, natural white light is emitted. When pumping xenon, krypton halogen, the heating temperature is from 4000 to 6400 K. Cold white light is emitted.
Light flow
The purpose of the light flux is lighting. It is created by the conversion of thermal energy. The unit of measure is Lumen (Lm). The increase in flux depends on the lamp power
Incandescent lamps of the same power emit different luminous flux. The higher the voltage, the higher the luminous flux.
History of creation
Interestingly, the first lamps used not tungsten, but a number of other materials, including paper, graphite and bamboo. Therefore, despite the fact that all the laurels for the invention and improvement of incandescent lamps belong to Edison and Lodygin, attributing all the merits only to them is wrong.
We will not write about the failures of individual scientists, but we will give the main directions to which the men of that time made efforts:
- Finding the best material for the filament. It was necessary to find a material that was simultaneously resistant to fire and was characterized by high resistance. The first thread was created from bamboo fibers, which were covered with a thin layer of graphite. Bamboo acted as an insulator, graphite - a conductive medium. Since the layer was small, the resistance increased significantly (as required). Everything would be fine, but the charcoal base of the coal led to rapid ignition.
- Further, the researchers thought about how to create the conditions of the strictest vacuum, because oxygen is an important element for the combustion process.
- After that, it was necessary to create detachable and contact components of the electrical circuit. The task was complicated due to the use of a graphite layer characterized by high resistance, so scientists had to use precious metals - platinum and silver. This increased the current conductivity, but the cost of the product was too high.
- It is noteworthy that the carving of the Edison base is still used today - marking E27. The first ways to create a contact included soldering, but in this situation it would be difficult to talk about quickly replaced bulbs today. And with strong heating, such compounds would quickly decay.

Nowadays, the popularity of such lamps falls exponentially. In 2003, the amplitude of the supply voltage was increased in Russia by 5%, to date, this parameter is already 10%. This led to a reduction in the life of the incandescent lamp by 4 times. On the other hand, if you return the voltage to the equivalent value down, then the luminous flux return will be significantly reduced - up to 40%.
Remember the training course - even at school, a physics teacher set up experiments, demonstrating how the luminescence of a lamp increases with increasing amperage supplied to a tungsten filament. The higher the current, the stronger the emission of radiation and more heat.
Structure
An ordinary lamp consists of the following structural elements:
- flask,
- vacuum or inert gas injected into it,
- filament,
- electrodes - current leads,
- hooks needed to hold the filament,
- leg,
- fuse,
- basement, consisting of a housing, an insulator and a bottom contact.
In addition to the standard versions of the conductor, glass vessel and conclusions, there are special lamps. Instead of a cap, other holders are used in them or an additional bulb is added.

The fuse is usually made of an alloy of ferrite and nickel and is placed in the gap at one of the current terminals. Often it is located in the leg. Its main purpose is to protect the flask from destruction in case of breakage of the thread. This is due to the fact that if it breaks, an electric arc is formed, leading to the melting of the remnants of the conductor, which fall on the glass flask. Due to the high temperature, it can explode and cause a fire. However, for many years they proved the low efficiency of fuses, so they began to be used less often.
Gas medium
If previously all incandescent lamps, without exception, were filled with vacuum, today this approach is used only for low-power light sources. More powerful devices are filled with inert gas. The molar mass of the gas affects the heat radiation by the filament.
Halogens are pumped into a bulb of halogen lamps. The substance with which the filament is coated begins to evaporate and interact with the halogens located inside the vessel. As a result of the reaction, compounds are formed which are repeatedly decomposed and the substance returns to the surface of the thread again. Thanks to this, it became possible to increase the temperature of the conductor, increasing the efficiency and the life of the product. Also, this approach made flasks more compact. The design flaw is associated with the initially low resistance of the conductor when applying electric current.
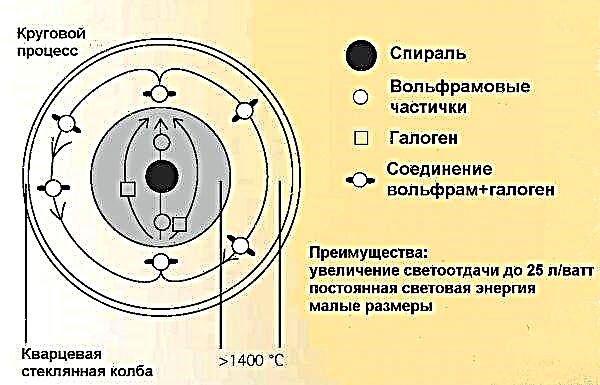
Filament
The shape of the filament may be different - the choice in favor of this or that is connected with the specifics of the bulb. Often they use a thread with a circular cross section, twisted into a spiral, much less often - tape conductors.
A modern incandescent lamp is powered by a tungsten or osmium-tungsten alloy filament. Instead of ordinary spirals, bispirals and trispirals can be twisted, which was made possible by repeated twisting. The latter leads to a decrease in thermal radiation and an increase in efficiency.
Advantages and disadvantages
Currently, there are many lighting fixtures. Most of them have been manufactured in the past few years using high technology, but classical LN still has many advantages or a combination of parameters that will be more suitable if used correctly:
- low enough price
- resistance to various temperatures,
- instant ignition
- don't flicker
- have different light modes.

But, unfortunately, incandescent lamps have their drawbacks:
- the main disadvantage is the rather low efficiency. For 100 W bulbs, the efficiency will be approximately 17%, for 60 W products this figure will be only 5%. One of the methods to increase the efficiency will be to increase the temperature of the filament, but in this case, the service life will decrease markedly,

- short service life
- increased temperature of the surface of the vessel, which can be at 100W light bulbs up to 250 ° C. This increases the risk of fire or explosion of lamps,
- sensitivity to the environment,
- the use of heat-resistant fittings.
The types and characteristics of incandescent lamps are described in detail below.
Principle of operation
During the passage of electric current through the spiral, it quickly heats up to high temperatures up to almost 2500 degrees. This is due to the fact that the spiral has a high resistance to current and it takes a large amount of energy to pass it.
Heat heats the metal (tungsten), and the lamp begins to glow. Since there is no oxygen inside the lamp, tungsten does not oxidize.

The efficiency of a 100 W incandescent lamp of the old model, where the rod of coal played the role of the glowing body, was much less than that of the latest models. This is due to the additional costs of convection. Spiral glow bodies have a lower percentage of such losses.
General, local purpose
Characteristics of general-purpose VL are prescribed in GOST 2239-79. These bulbs are used to connect the main lighting of domestic and public places, as well as street space, to the lamps.
The main voltage can be 127 and 220 V. The assortment of products is divided into groups depending on the types of glow body (spiral or bispiral) and medium (vacuum, gas).

The shape of the vessel, the installation method, the brand of the product and the type of cap are selected for reasons of cost, practicality of the technology, for at least 100 hours of operation. It must be emphasized that in recent years the effectiveness of such lamps is evaluated by many characteristics.
LN for local use, produced under GOST 1182-78, the voltage should not be higher than 36 V, and for industrial premises where there are easily combustible substances - 12 V. The power of local lamps is limited and will be 15, 25, 40 and 60 watts. The service life of each incandescent lamp should be at least 75% of the average duration of the glow.
For street lighting, more powerful lamps are taken so that you do not have to change them every month or two. Since this is a rather time-consuming process.

Decorative
Decorative bulbs can be of various shapes, round, oval, spiral and so on. The source of radiation will be a tungsten filament. With the help of it, a cozy and warm light is obtained in the room. Basically, the factory produces designer products for the classic E27 base, but there are models for the E22 and E40 base.
The voltage required for correct operation is 220 V. The term of use of decorative products with a tungsten filament can be in the range of 2000-3400 hours, but not more. The lighting temperature is characterized by a parameter of 2700 K.
Such products are often used to decorate rooms, flights of stairs or Christmas trees. Large shopping centers use decorative bulbs suspended from high ceilings. It looks truly beautiful and at the same time cozy. They will harmoniously combine with the Loft style in the house or apartment.
Illumination
These incandescent lamps are produced with a colored inner layer of the bulb and are necessary for New Year's garlands or for illuminating stairs, shops and display cases. It has a wide range of color, there are cold, white, day and night shades. Sufficiently high service life of up to 25,000 hours, with proper operation. The main disadvantage will be a difficult installation. The closer the end of the product’s life, the weaker it will work. Light will begin to scatter poorly.

Lamp bases
Incandescent lamps can also have various types of cap. For example, threaded plinths. They are indicated by the Latin letter E (Edison's base). As well as socle bayonet type. They are designated by the Latin letter B. The bayonet-type plinths (pin base) have two side pins - contacts. And also one or two additional lower contacts. Typically used in cars. Incandescent lamps used to illuminate a home usually have a threaded base E. Most often, the base E type is of two sizes. This is E14 (minion) and the usual middle base is E27. The number indicates the outer diameter of the cap in millimeters. The large base E40 is usually used in production, and in everyday life, perhaps, only in floodlights.
Advantages of an incandescent lamp
- Low price
- Turn on and switch instantly (Quick Start)
- Work from both direct and alternating current
- Wide voltage range application
- No flicker when used in AC power
- No humming when working on AC power
- Does not require ballasts
- High color rendering index Ra 100 (Colors of surrounding objects are perceived as in sunlight)
- Stable operation both in large frosts and in extreme heat
- Ability to control brightness and smooth start using a dimmer
- It does not contain toxic substances and does not require special disposal.
For all its shortcomings, an incandescent lamp has a lot of advantages and can occupy its niche in our homes, together with other types of lamps. The excitement around the extreme inefficiency of an incandescent lamp and the need to completely replace it with LEDs is greatly inflated and exaggerated. Most of the instruments and devices that we use have low efficiency. In fact, more than one device does not have an efficiency of 100%. The low efficiency of incandescent lamps and the short duration of their service are more than redeemed by their low price.
Related posts
You can read entries on similar topics under the heading - Lighting
Specifications
It is interesting to observe the dependence of light energy and lamp power. The changes are not linear - up to 75 W, the light output increases, when exceeded, it decreases.
One of the advantages of such light sources is uniform illumination, since in almost all directions light is emitted with the same intensity.

Another advantage is associated with the pulsation of light, which at certain values leads to significant eye fatigue. The normal value is considered a ripple coefficient not exceeding 10%. For incandescent lamps, the maximum parameter reaches 4%. The worst indicator is for products with a power of 40 watts.
Among all the available electric lighting devices, incandescent lamps heat up more. Most of the current is converted into thermal energy, so the device is more like a heater than a light source. Luminous efficiency is in the range from 5 to 15%. For this reason, certain laws are prescribed in the law prohibiting, for example, the use of incandescent lamps of more than 100 watts.
Usually, a 60 W lamp, which is characterized by a slight heating, is enough to illuminate one room.
When considering the spectrum of radiation and comparing it with natural light, two important points can be made: the luminous flux of such lamps contains less blue and more red light. Nevertheless, the result is considered acceptable and does not lead to fatigue, as is the case with daylight sources.

Operational parameters
When operating incandescent lamps, it is important to consider the conditions for their use. They can be used indoors and outdoors at a temperature of at least –60 and not more than +50 degrees. Celsius. In this case, air humidity should not exceed 98% (+20 deg. Celsius). Devices can work in one circuit with dimmers designed to regulate light output due to changes in light intensity. These are cheap products that can be independently replaced even by an unskilled person.
There are several criteria for the classification of incandescent lamps, which will be discussed below.
Depending on the lighting efficiency, incandescent lamps come in (from worst to best):
- vacuum
- argon or nitrogen-argon,
- krypton
- xenon or halogen with an installed infrared reflector inside the lamp, which increases the efficiency,
- with a coating designed to convert infrared radiation into the visible spectrum.

There are much more varieties of incandescent lamps associated with functional purpose and design features:
- General purpose - in the 70s. last century they were called "normal-lighting lamps." The most common and numerous category are products used for general and decorative lighting. Since 2008, the production of such light sources has significantly decreased, which was associated with the adoption of numerous laws.
- Decorative purpose. Flasks of such products are made in the form of elegant figures. Most often there are candle-shaped glass vessels with a diameter of up to 35 mm and spherical (45 mm).
- Local destination. By design, they are identical to the first category, but they are powered by a reduced voltage - 12/24/36/48 V. Usually used in portable lamps and devices that illuminate workbenches, machines, etc.
- Illumination with painted flasks. Often, the power of the products does not exceed 25 W, and for staining the internal cavity is covered with a layer of inorganic pigment. It is much less common to find light sources, the outer part of which is painted with colored varnish. In this case, the pigment fades very quickly and crumbles.

- Mirrored. The flask is made in a special form, which is coated with a reflective layer (for example, by spraying aluminum). These products are used to redistribute the light flux and improve lighting efficiency.
- Signaling. They are installed in light-signal products designed to display any information. They are characterized by low power and are designed for continuous operation. Today, they are almost useless due to the availability of LEDs.
- Transport. Another extensive category of lamps used in vehicles. They are characterized by high strength, resistance to vibration. They use special plinths, guaranteeing a solid mount and the ability to quickly replace in cramped conditions. They can be powered from 6 V.
- Spotlights. High-power light sources up to 10 kW, characterized by high light output. The spiral is stacked compactly to provide better focus.
- Lamps used in optical devices, for example, film projection or medical equipment.
Special lamps
There are also more specific varieties of incandescent lamps:
- Switching - a subcategory of signal lamps used in switchboards and acting as indicators. These are narrow, oblong and small-sized products having parallel contacts of a smooth type. Due to this, they can fit in buttons. Marked as “KM 6-50”. The first number indicates voltage, the second - amperage (mA).
- Perekalnaya, or photolamp. These products are used in photographic equipment for the normalized forced mode. It is characterized by high light output and color temperature, but a short life. The power of Soviet lamps reached 500 watts. In most cases, the flask is matted. Today, almost never used.
- Projection. Used in slide projectors. High brightness.
A double-thread lamp comes in several varieties:
- For cars. One thread is used for dipped, the other for high beams. If we consider lamps for the rear lights, then the threads can be used for the brake light and side light, respectively. An additional screen can cut off the rays that in the low beam lamp can blind drivers of oncoming cars.
- For airplanes. In the landing light, one thread can be used for small light, the other for large, but requires external cooling and short operation.
- For railway traffic lights. Two threads are needed to increase reliability - if one burns out, the other will glow.

We continue to consider special incandescent lamps:
- Lamp-headlight - a complex design for moving objects. It is used in automobile and aviation equipment.
- Low inertia. Contain a thin filament. It was used in optical recording systems and in some types of photo telegraph. Nowadays it is rarely used, since there are more modern and improved light sources.
- Heating. It is used as a heat source in laser printers and copiers. The lamp has a cylindrical shape, is fixed in a rotating metal shaft to which toner paper is applied. The shaft transfers heat, which causes the toner to diffuse.
The electric current in incandescent lamps is converted not only into light visible to the eye. One part goes to radiation, the other transforms into heat, the third into infrared light, which is not fixed by the visual organs. If the temperature of the conductor is 3350 K, then the efficiency of the incandescent lamp will be 15%. A conventional 60 W lamp with a temperature of 2700 K is characterized by a minimum efficiency of 5%.
The efficiency is enhanced by the degree of heating of the conductor. But the higher the heating of the thread, the shorter the service life. For example, at a temperature of 2700 K, a light bulb will illuminate 1000 hours, 3400 K - many times less. If you increase the supply voltage by 20%, then the glow will increase twice. This is irrational, since the service life is reduced by 95%.
Advantages and disadvantages
On the one hand, incandescent lamps are the most affordable light sources, on the other hand, they are characterized by a lot of shortcomings.
- low cost,
- there is no need to use additional devices,
- ease of use
- comfortable color temperature
- resistance to high humidity.
- fragility - 700-1000 hours, subject to all the rules and recommendations for use,
- low light output - efficiency from 5 to 15%,
- fragile glass bulb
- the possibility of explosion during overheating,
- high fire hazard,
- voltage drops significantly reduce the life of the device.
Varieties of incandescent lamps.
Incandescent lamps are divided into:
- Vacuum
- Argon (nitrogen-argon),
- Krypton (+ 10% brightness from argon),
- Xenon (2 times brighter than argon),
- Halogen (composition I or Br, 2.5 times brighter than argon, high service life),
- Halogen with two flasks (improved halogen cycle due to better heating of the inner bulb),
- Xenon-halogen (composition Xe + I or Br, up to 3 times brighter than argon),
- Xenon halogen with infrared reflector,
- Incandescent coating, converting infrared radiation into the visible range. (new)
Signaling
Signal lights are mainly used in various industries. The simplicity of the device and the large model range help to choose products for work in different areas of production. Lamps can be mounted on machines, remote control, on special vehicles and so on. Very often used in mechanical engineering, woodworking or metallurgy.
Attention! You can connect one light bulb to perform several operations, or use at the same time 2-3 products for various purposes. Based on the scope of use, the color and shape of the lamp is selected.
Modern incandescent lamps are made specifically for industrial use, which gives a number of advantages over conventional light signaling lamps:

- various color modes giving a more informative signaling,
- many choices of lights
- suitable for any electrical network,
- easy installation on machines with screw connection system,
- the ability to replace contacts,
- the use of LED bulbs of increased brightness to improve visibility in any industrial areas,
- convenient housing with the ability to select the right size,
- energy saving
- ease of use.
Mirrored
The mirror-type product differs from other LVs in the rare bulb shape, as well as the presence of a coating with light reflection, which looks like a thin foil.
This coating is sprayed onto the lamp in order to scatter its light radiation in the room, to more correctly distribute it within a certain point, so that it is possible to clearly illuminate a certain room.
To get this option in a conventional lamp, you need to put a large reflector behind it.
Mirror bulbs are mainly connected to directional light fixtures used for spot lighting stores, so that the necessary zones are illuminated. They are also used for offices, stairs, architectural monuments.
Mirror lamps can be multi-colored and transparent, matte, or with the effect of UV rays. They are produced by all famous factories of lighting devices.

Transport
As lighting for cars, transport incandescent lamps are used. In the electric circuit, the body filament warms up and at the peak temperature the glow begins. The energy of the light beam perceived by the ordinary eye will be small. The bulk of the energy will be in the form of heat.
The transport lamp incorporates a bulb, several filaments, a base and conclusions.
Filament bodies in double-stranded products can work in different ways. Two-filament bulbs are equipped with car lights, a lamp in the cabin.
The filament must withstand elevated temperatures, and also quite small. Therefore, it is produced from medium-sized tungsten wire curled into an elongated spiral.

The spiral is connected to the electrodes and basically has the form of a straight line or an arc of a semicircle. The melting point of tungsten will be about 4000 degrees. During operation, the spiral heats up to 2500-2800 ° С. With an increase in the temperature of tungsten, the brightness and luminous efficiency of the rays on the LN increases. But if the indicators exceeded 2500 ° C, tungsten will quickly evaporate and remain on the walls of the glass vessel, which results in a layer of plaque, which will reduce the quality of lighting. The service life of such products is usually from 4 months to six months. Depends on the manufacturer and the quality of the production raw materials.
Double thread
Such a product can be of three types:

- for cars. One thread is used for low beam, the second - for high beam. If we talk about lamps for the rear signals, then the threads can be used for the brake light and the side light are the same. An additional screen will remove the rays that in the dipped beam signal can dazzle the owners of oncoming cars,
- for an aircraft. In the landing light, the first thread is used for small lighting, the second - for large, but if the second works for too long, then cooling may be necessary, otherwise a fire may occur,
- for traffic lights on the canal road. Both threads are needed to increase reliability — if one burns, the other will work.

Flask
A glass bulb gives protection to the spiral from the harmful effects of air; when it is deformed, the glow body oxidizes and quickly explodes. The composition of the lamp bulb varies, it can be filled with vacuum or a gas medium. The first incandescent lamps were produced with a vacuum capacity, but their power was not high. Nitrogen-argon substance or exclusively argon is used to fill modern products. Some types of bulbs can fill with krypton or xenon. The heat transfer of the bulb depends on the molar mass of the filler.

Gas medium
The gas atmosphere in the lamp must be inert. Since the temperature of the spiral reaches 2500 degrees, it can respond to any gas, but not inert. Therefore, argon is most often used for filling.
If water suddenly enters a hot or working lamp, it may burst due to gas.
Xenon lamps sometimes fill, but it will be relatively expensive.
In many lamps, the gas environment will be a protection function. In others, due to the electric discharge, beautiful color radiation is obtained. The hue will depend on the properties of the inert gas.
Glow body
Types of glow bodies can be different and depend on the functional purpose of the bulbs.

The most popular will be of oval cross-section wire, but sometimes there are also tape bodies of glow (they consist of a metal tape).
As already mentioned, the first glowing bodies were made from coal. In modern LVs, only incandescent bodies made of tungsten, less often of osmium-tungsten material, are used.
To reduce the size of the filament, it is usually done in the form of a spiral, sometimes it is subjected to repeated processing, from which a bispiral is obtained. The efficiency of such products is higher due to lower heat losses during convection.
Electrical parameters
The luminous efficiency of such products is quite low. It will be the lowest among popular light bulbs and is in the range from 5 to 10 lm / W. The increased brightness of the glow body in combination with its small size allows the use of products in searchlights.

LVs have a wide range of medium voltages and powers. This type of product can function in a wide range of ambient temperatures, which is limited only by the thermal stability of the raw materials used in its production (-100 ... + 350 degrees). The light radiation of the LV is corrected by the transformation of the operating voltage.
With this minus, there will be an increased operating temperature and the amount of heat generated during combustion. Since the temperature of the bulbs is high, they become ulcerated by the action of water or a sharp transfer of degrees (from minus to plus and vice versa).
In the modern world, many have long abandoned the use of incandescent lamps. In developed cities, only 20% of people use such products. Everyone is switching to halogen lights.
When the bulb is turned on, the glow body is at normal temperature, then the resistance of the product will be much less than the working resistance. During power-up, a large amount of current flows. As the thread splits, its resistance increases, and the current decreases.

Unlike the latest products, older models of incandescent lamps with carbon spirals when turned on had the reverse process with increasing current. The increasing function of the resistance of the glowing body allowed the use of a lamp as a primitive electric stabilizer.
Shelf life
The service life of a product depends on its quality. LN should be stored in a cardboard box. This is necessary in order not to accidentally break it, or so that it does not give an imperceptible crack that will ruin all the work. Because of such a crack, the gas will evaporate, as a result, after the bulb is screwed into the ceiling, it will work for no more than 2-3 hours. Observe safety rules when screwing the lamp into the lampshade. Children should not be allowed to participate in this process, and it is also advisable to completely turn off the electricity in the room.
Note! Used bulbs must be disposed of correctly; throwing them away with food waste is not allowed. Each city has special tanks for such waste.
If you follow all the rules of storage and use, the lamp will last as long as possible, without defects.

Incandescent lamp device
The main details of which the design of the LV consists of a base, a vessel, electrodes, holders for filament, an incandescent body, contacts and insulation. In Figure 10, you can see the structure of the bulb.
Before buying a lamp, it is advisable to consult a specialist. It is not recommended to give a choice to an unknown manufacturer, as defective products that will not work as expected, or even burst when energized, can be caught. Quality manufacturers always give a guarantee of at least 30 days for incandescent lamps. The buyer has the full right to exchange the product or refund if the lamp was less than 10 hours or it burned out instantly.
In conclusion, it should be noted that incandescent lamps have long ceased to be popular among people. However, it must be emphasized that among such products there is a huge selection for cars, street lighting, aircraft and so on. Unfortunately, flaxseed cannot be used near wood products. Since sometimes there is strong heating and rupture of the spiral, because of which an emergency situation may occur.



