To determine how much sand and cement are needed per 1 cubic meter of mortar, it is important to know its purpose. For the preparation of masonry, plaster, foundation and other types of mixtures, a different ratio of dry materials is used. The consumption of sand and cement per 1 m3 of solution varies for each type of work, and often other dry or liquid compositions are added to the composition, which increase moisture resistance, strength, change the curing rate of the mixture, etc.
What determines the consumption of cement for different solutions
The preparation of cement mortar, the proportions of which may vary, require a clear adherence to the technology and the correct determination of the ratio of components. For the use of concrete of different grades, a different amount of cement and sand is used. Remembering the proportions of cement and sand is not enough for quality construction, it is better to understand the principle.
 Requires a clear adherence to the technology of preparation of cement mortar
Requires a clear adherence to the technology of preparation of cement mortar
The main factors affecting consumption:
- the amount of fillers in the mixture. The greater the proportion of crushed stone, sand, the higher the cement consumption per 1 m3 of solution. Cement is a binder of components that is responsible for bonding all fillers together. The ratio of bulk mixtures determines the amount of cement,
- brand of cement. As the brand increases, the strength of the final structure increases. It is worth remembering that the brand of the final mixture is much lower than dry cement, since sand is added to the composition, and gravel or slag can also be added,
- brand of solution. The cement-sand mortar also has a separation by brand. For all types of work, GOST has recommended brands. After determining the desired brand of building mixture, you can choose the right brand of cement. For example, to obtain a mixture of M100 from cement M500, you will need to mix 1 part of Portland cement, 5.8 parts of sand and 8.1 parts of crushed stone. If the final goal is a solution of M450, a proportion of cement M500 (C: P: U) 1: 1.4: 2.9 will be required,
The density of cement plays a secondary role here, as it directly depends on the brand of cement, but it must be known in the calculation process.
Conclusion: how much cement is required per 1 m3 of mortar depends on the required strength of the mortar and the grade of the initial mixture.
Variety and brands of mixtures
The introduction of the concept of “cement grade” helps to calculate the consumption of cement per cube of the solution with knowledge of the input parameters. To prepare a mortar with the same construction characteristics from different grades of cement mixture, different proportions of fillers will be required. Cement is produced in production, starting from the M100 brand, but due to the low structural strength the material is practically not used.
The most popular are cements M400 and M500, but some other types have also become widespread. The choice of mixture depends on the scope of the material.
The main areas of use of cement brand:
- M300 cement is used in installation construction, as well as during the manufacture of monolithic structures,
- M400 cement is successfully used in monolithic construction and during the preparation of reinforced concrete,
- M500 cement is actively used in the construction of buildings or slabs, which must be resistant to moisture or are in water. The scope of this concrete mix is quite wide: the creation of sidewalks, the construction of asbestos-cement structures, the formation of large concrete masses and all kinds of foundations,
 Cements M400 and M500 are the most popular.
Cements M400 and M500 are the most popular. - M600 cement is used to create prefabricated structures and foundations, which are under high load,
- M700 is a suitable brand of cement for the construction of highly loaded and stressed buildings.
Consumption rates of materials per cubic meter of different solutions
Today, there are 4 main areas of concrete use: foundation, masonry, screed and plaster. In each case, special requirements are made to the building mixture, which makes the choice of cement and its consumption different. The greatest cement consumption per cube of concrete occurs when necessary to make masonry or plaster. The material consumption per 1 m3 of the foundation solution is slightly lower due to the use of a large fraction of the filler: slag, crushed stone or gravel.
GOST has records on cement consumption rates per 1m3 of mortar, taking into account the purpose of the mortar. Designation of concrete in a cube. meters is a common measurement system.
Consumption standards for 1 m3 using cement M500:
- on M100 - 170 kg,
- on M150 - 200 kg,
- on M200 - 240 kg,
- on M250 - 300 kg,
- on M300 - 350 kg,
- on M400 - 400 kg,
- on the M500 - 450 kg.
The rates of consumption of cement and sand per cube of mortar for the foundation
Calculation of cement on a foundation calculator is the simplest way to understand how much material is needed and the amount of necessary components. Calculation of concrete can be done with high accuracy and manually.
To determine how much cement is needed per 1 m3 of solution, we recommend that you follow a simple instruction:
 Cement consumption rates for the foundation
Cement consumption rates for the foundation
- We determine the appropriate brand of cement mortar. Usually, during the creation of the foundation, it is advisable to use the M100-M300 solution. For low-level buildings, M100 is enough, if it is planned to build several floors - M150, and M200 and higher is used in the construction of multi-story buildings and any structures that have high strength requirements. If the foundation is built under a wooden building, M50 mortar is enough.
- We select the brand of cement. For standard tasks, the M300-M400 in a proportional part of cement to sand 1 to 3 is suitable. When using cement M500 - 1 to 5.
How many kg of cement in 1 m3 of solution:
- in M50 when using M400 - 380 kg,
- in M100 in the preparation of concrete from M300 cement - 214 kg,
- in M200 with cement M400 - 286 kg,
- in M300 with M500 - 382 kg.
The data are presented if 2-4 parts of sand and 3 parts of crushed stone are included in the cube.
The rates of consumption of cement and sand per cube of mortar for masonry
The ratio of 1 to 4 is most often used for the preparation of cement mortar for wall construction. Thus, the cement consumption per cube will be 0.25 m3 or 325 kg, and the sand consumption per 1 m3 of mortar will be 0.75 m3 or 1200 kg.
Table 1: Mortar consumption for walls of different thicknesses
| Thickness in bricks | Consumption, m3 |
| 0,5 | 0,189 |
| 1 | 0,221 |
| 1,5 | 0,234 |
| 2 | 0,24 |
| 2,5 | 0,245 |
To calculate how many bags of cement are needed, it is enough to multiply 325 kg by the consumption per cube, for example, walls in one brick - 0.221. It will turn out 72 kg of cement for laying 1 m3 of wall, provided that there are no other components in the composition (lime, clay, etc.).
The consumption rates of cement and sand per cube of mortar for screed
Cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of mortar is calculated according to the same rules as in previous mixtures. The recommended mixing ratio is 1 to 3. Difficulties in the calculations often appear even at the stage of determining the volume of the solution, so let's consider a good example. It is necessary to fill the surface of 3x4 m or 12 m2. The layer thickness will be 30 mm.
 Cement consumption rates for screed
Cement consumption rates for screed
Calculation of cement for screed from an example:
- We calculate the required volume of the solution: 12 m2 * 0.03 m = 0.36 m3.
- We determine the brand of cement, the M200 solution is often used, and we use it as an example. We will cook from the M500, and according to the standards, the consumption will be 410 kg.
- We consider the required number of cement bags: 410 kg * 0.36 m3 = 148 kg - these are 6 small or 3 standard bags of 50 kg each.
- Determine the cost of sand. To do this, we multiply the specific gravity of 1 m3 of sand by the required amount of the finished mixture: 1600 kg / m3 * 0.36 m3 = 576 kg, and since the proportion of sand in the total solution is 75%, we multiply by 0.75 - 432 kg of sand. The consumption of sand per 1 cubic meter of solution is approximately 1200 kg / m3.
Cement and sand consumption rates per cube of mortar for plaster
The consumption of cement per 1 m2 of plaster strongly depends on the quality of the wall covering, the required layer thickness and the number of large pits. Again, for clarity, we give an example of calculation, remembering that a 1 to 4 mixture is usually used. Input parameters: it is necessary to cover 60 m2 of the wall with plaster 2.5 cm thick.
Calculations of cement consumption per 1 m3 and sand:
- The number of materials in cubes. For 1 m2, 1 * 0.025 = 0.025 m3 of solution will be required, where the fifth part is cement and the rest is sand. Using elementary mathematics, we determine that it will require 0.02 m3 of sand and 0.005 m3 of cement.
- The entire wall area will require: 0.02 * 60 = 1.2 m3 of sand and 0.005 * 60 = 0.3 m3 of cement.
- The specific gravity of cement is on average 1400 kg / m3 (fresh 1100-1200 kg / m3, and caked 1500-1600 kg / m3). Determine the consumption of cement: 0.3 * 1400 = 350 kg.
- Required weight of sand: 1.2 * 1600 = 1920 kg, recall 1600 kg / m3 - specific gravity of sand.
All calculations are simple, it is only important to choose the brand of the initial mixture and the desired brand of solution at the outlet. Everything else is easily calculated in a few mathematical steps.
Selection of the composition of the solution per 1m3 of sand
To implement the calculator, data and a calculation algorithm were taken from:
1. We determine the consumption of binder (cement) per 1m3 of sand, depending on the selected brand of mortar and brand of cement.
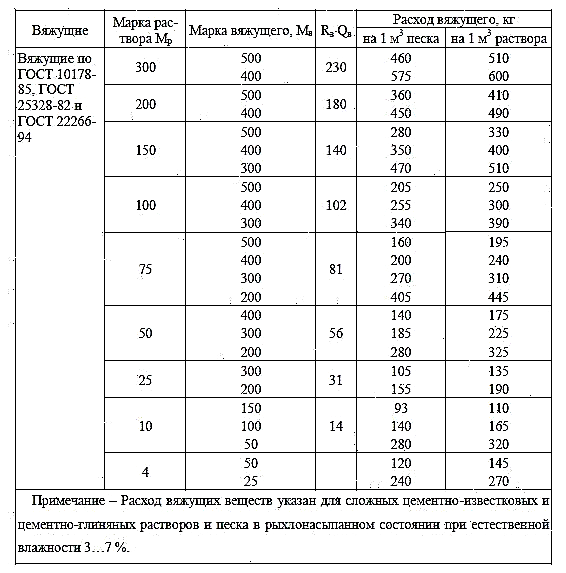
We determine the cement consumption per 1m3 of sand according to the formula:
2. We determine the volume of lime per 1 m3 of sand according to the formula:
Where Qv - binder (cement) consumption per 1 m3 of sand, kg
Vd —Inorganic additive (lime) per 1 m3 of sand, m3.
We determine the mass of lime per 1m3 of sand according to the formula:
Where Qd - consumption of additives (lime) per 1 m3 of sand (kg),
λ - bulk density of the additive (lime) kg / m3,
3. We make the proportion of the volume parts of the solution

You can also use the table of ready-made proportions in volume ratios (table 4 SP82-101-98)
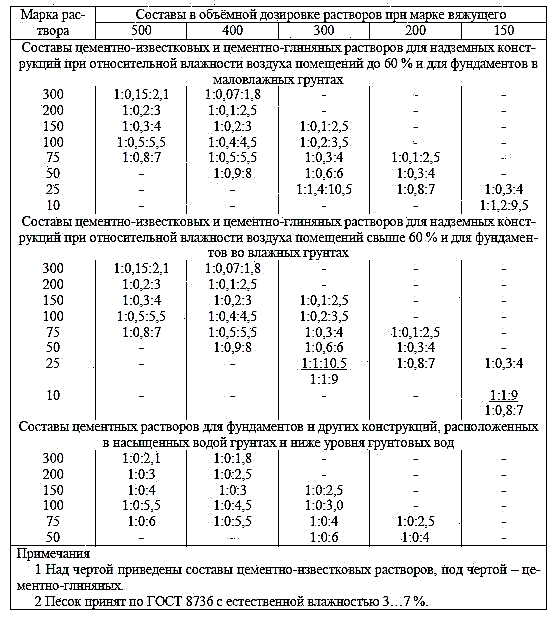
4. Determine the flow rate of water per 1 m3 of sand.

The approximate water consumption in SP82-101-98 is shown for a mixture with mobility P3 (9-10cm cone draft depth). This mobility according to GOST 28013-98 is suitable for masonry made of solid brick and ceramic stones. Water consumption for a different mobility of the mixture is determined as a result of test batches. We can choose the mobility we need, depending on the purpose of the solution, according to the table presented in GOST 28013-98

"Grandfather method" or the current SNiP?
Experience is a good thing, but you should not forget about building codes. They take into account all the factors associated with the preparation of mortars and concrete (cleanliness, fineness, moisture of sand and gravel, activity of cement and water quality).
Therefore, when preparing for work on filling the foundation, screed or laying walls, do not be lazy to look at the guest tables. In them you will need only one or two lines. They clearly describe what cement consumption should be per cubic meter of mortar to obtain the necessary strength (grade).
Here is a simple “squeeze” from SNiP, which will help to cook high-quality mortar for masonry and screed. After studying it, remember that the given consumption rates are slightly different from practical values.
Cement grade
Grade of solution
The consumption rate of cement for the manufacture of 1m3 solution

The reason is that they are derived from standard conditions of preparation (air temperature + 23 ° C, sand of medium grain size, perfectly clean, its humidity is not more than 7%, etc.). It is not realistic to ensure the normative parameters of batches at a construction site, so it is better to buy cement with a small margin (10-15%).
The answer to the question, how much cement and sand is needed per cube of concrete will be given to you by such standards:
Concrete grade
Cement consumption M500 kg / 1m3
When making concrete, it is important to know not only the amount of cement, but also the normative volume of sand and gravel. The following table will be useful for calculations.
Volume proportions for various grades of concrete
Concrete, brand
The ratio of cement / sand / gravel in liters
cement M 400
cement M 500
Required sand consumption per 1m3 of solution - 1 cubic meter. Some developers are mistaken, believing that the volume of cement increases the volume of the finished mixture. This is not true. Cement has a very fine grinding, so it is distributed in the voids between the sand, without increasing the total volume of concrete and mortar. Therefore, for 1 m3 of sand, we can add 200 and 400 kg of cement, obtaining the same 1 cube of the solution.
Water is added to the mixture in a simple proportion - half of the total weight (not volume!) Of cement. In this case, you need to take into account the actual humidity of the sand and pour water in small portions so that the solution or concrete does not turn out to be too liquid.
The consistency of the solution according to the norms is determined by the amount of precipitation of a standard metal cone, lowered into the mixture. At a construction site, you are unlikely to be able to conduct such a test. Therefore, just remember that the density of the masonry mortar should be such that it is not too hard, but sufficiently plastic and does not leak from the seams. For screed, mortar and concrete should be of medium density so that they can be easily compacted and leveled as a rule.
What does cement consumption depend on?
Intuitively, everyone understands that the consumption of this binder depends on the degree of structural strength that we are going to build. Therefore, for the foundation, we need concrete grade not lower than M300, and for the screed there will be enough mortar with a strength of 150 kg / cm2 (M150).
The brand of cement that will be used matters. The higher it is (seen from the tables), the less the binder will be consumed.
Cement consumption for plaster
A “classic” stucco mortar consists of three parts of sand and one part of cement (1: 3).

If the average layer thickness does not exceed 12 mm, then 1.6 kg of cement M400 or 1.4 kg of cement M500 should be weighed per 1 m2 of plaster. The volume of solution per 1 m2 is not difficult to calculate: 1 m2 x 0.012 m = 0.012 m2 or 12 liters.
Consumption of cement for masonry
When preparing a cement-sand mortar for masonry, take into account that for the construction of 1 m2 of a wall 1 brick thick (250 mm), at least 75 liters of M100 grade mortar will be required. Proportion of cement (M400) - sand here is 1: 4. The cement consumption for brick laying with this ratio will be 250 kg per 1 cube of sand.

Water, as we have already said, is taken at the rate of 1/2 of the total weight of the cement used.
Translating into “bucket norms” understandable to everyone, we say that for one 10-liter bucket of cement (M500) we need four buckets of sand and 7 liters of water. We consider the amount of water based on the weight of cement in the bucket (10 liters x1.4 kg x 0.5 = 7 liters).
To quickly determine the need for cement masonry mortar for walls of different thicknesses (per 1 m3), you can use the following table:
Wall thickness in bricks
How many cement bags to buy?
Until it comes to kneading, it is important for the developer to know how many bags of cement will have to be purchased. It should also be based on standard consumption rates.

Let's say we need to calculate the cement consumption for screed. The optimum proportion for high strength is 1: 4. Cement for this work we need ¼ cube. To convert cubes to kilograms, an average indicator of the bulk density of the binder is used: 1.4 kg of cement in 1 liter.
1/4 of the cube is 250 liters. Multiplying them by 1.4 kg, we get 350 kg of cement. So, we just have to buy 350/50 = 7 bags of cement (50 kg each) or 14 bags of 25 kg each.

You can calculate the consumption of a binder per 1 m2 of screed "reverse motion". With a thickness of 10 cm, pouring one "square" will require 0.1 m3 of solution. It contains 10 times less cement than in 1 cubic meter: 350 kg / 10 = 35 kg. For a screed with a thickness of 5 cm, we need 35/2 = 17.5 kg of M500 cement.
The rate of cement consumption is strongly influenced by such an indicator as activity. It is determined experimentally by kneading control samples and testing them for strength. For an ordinary developer, this method is not suitable. The practical method that you need to use when buying and before use is the shelf life.
Loss of cement activity can reach 20% in one month. Therefore, having kept this material in the garage for three months, instead of the 500 grade indicated on the label, you will receive the 400 grade. Using such a binding material for mortar or concrete, take the consumption rate for this (lowered) grade. If cement has been waiting for its "finest hour" for six months, then for nothing, except for disposal in a landfill, it is unsuitable.
Vigilance should also be shown when buying a binder, requiring the seller to buy a certificate of the batch, which indicates the factory date of release.